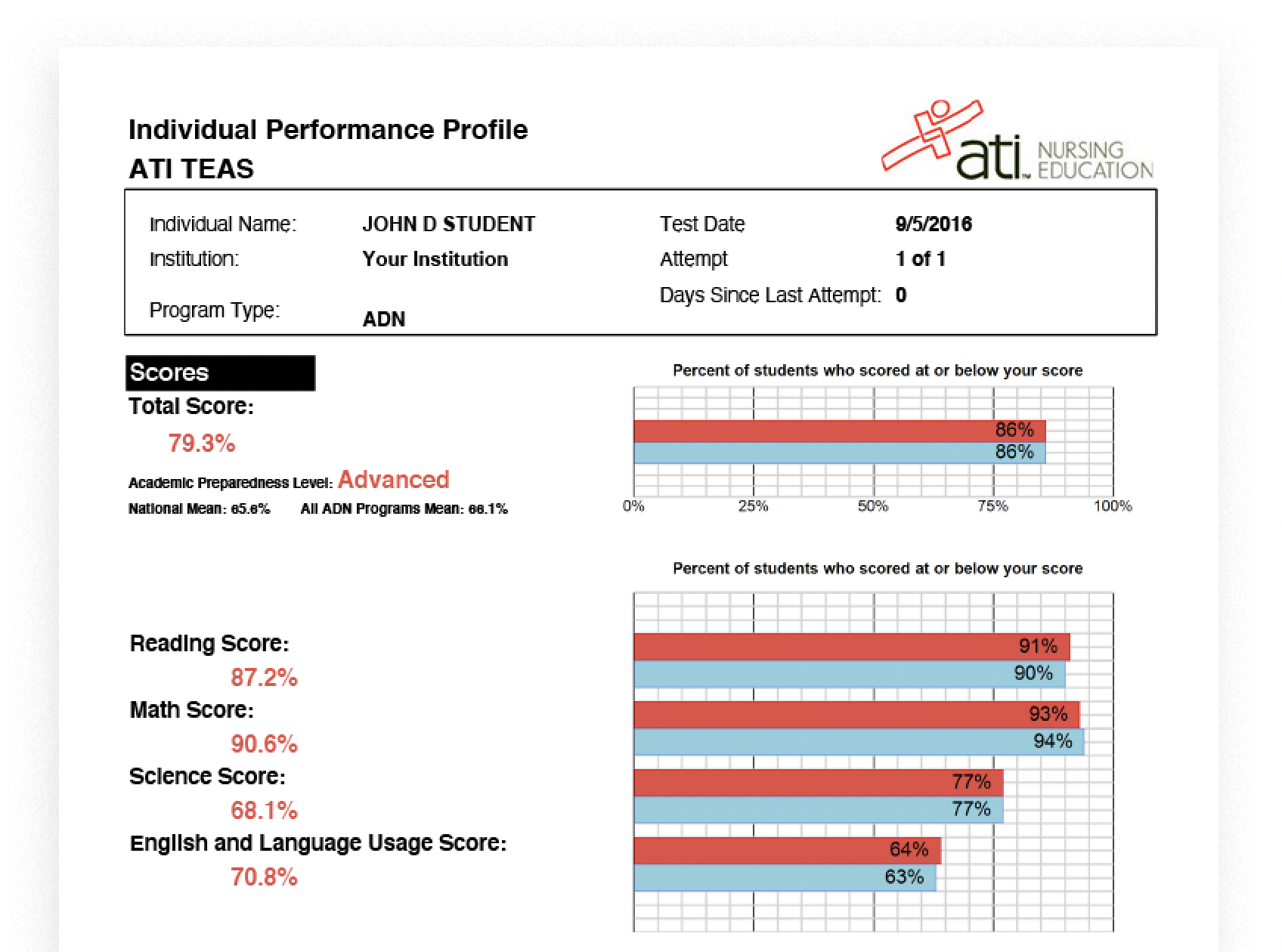
Examination Mac OS
Apple certification programs are IT professional certifications for Apple Inc. products. They are designed to create a high level of technical proficiency among Macintosh service technicians, help desk support, technical support, system administrators, and professional users. Chumba casino lawsuit. Apple certification exams are offered at Prometric testing centers and Apple Authorized Training Centers, as well as online through Pearson Vue.
Hardware Certifications[edit]
These certifications are designed for individuals interested in becoming Apple service technicians, help desk, desktop support, or Macintosh consultants who need all-around experience in servicing Macintosh computers. It includes two separate certifications.
Apple Certified Macintosh Technician[edit]
This certification is for the repair and diagnostics of all Macintosh desktops, portables, and servers. https://softlive.mystrikingly.com/blog/chrome-download-win7-64-bit. This certification is required to perform warranted hardware repairs for an Apple Authorized Service Provider.
- Required exams
- Apple Service Fundamentals Exam (Pearson Vue exam: #SVC-16A)
- ACMT 2016 Mac Service Certification Exam(Pearson Vue exam: #MAC-16A)[1][2]
Mac OS Download; Examlock. Assessment Tools for Learning Systems. BEFORE YOU INSTALL This brief video explains the basic features of LockDown Browser and why it's used at your institution. TERMS & CONDITIONS. ExamView Pro 1.0 for Mac is available as a free download on our application library. The most popular version among the application users is 1.0. This Mac app is a product of eInstruction® Corporation. Our built-in antivirus scanned this Mac download and rated it as virus free. The application relates to Education Tools. Mac Forensics 1. MacIntosh Forensics A presentation by Special Agent Thomas R. Nesbitt Federal Bureau of Investigation With assistance from presentations Prepared by John Mallory And Wayne Mitchell.
Previously, the hardware certification came in the combination of Apple Certified Desktop Technician (ACDT) and Apple Certified Portable Technician (ACPT), but has been combined into a single hardware certification. This certification also includes an extensive knowledge of Apple's operating system OS X 10.6 Snow Leopard including its installation, settings, troubleshooting, and applications.
Before November 2014, the Apple Certified Macintosh Technician did not cover the Retina MacBook Pro lineup, as well as all Macs released after 2012. To repair a Late-2013 13-inch MacBook Pro with Retina Display, one must be an Apple Certified Macintosh Technician and pass an exam for repairing 13-inch Retina MacBook Pros (Late 2013 to Early 2015). All technicians who received certification after November 20, 2014 are certified to repair any Mac released before 2015.[3]
Pro Apps certifications[edit]
These certifications are designed for individuals who need a high skill-level in the use of Apple's pro applications or for professionals who provide support for Final Cut Pro software and peripheral devices.
- Apple Certified Pro
- Final Cut Pro X
- Logic Pro X
- Logic Pro X 10.1
- Motion 5 (Level One)
IT Professional Certifications[edit]
These certifications are designed for IT professionals who support Mac OS X or who perform Mac OS X desktop support and troubleshooting, such as help desk staff, system administrators, service technicians, and service desk personnel. Each certification is specific to the version of OS X it relates to; an administrator who was qualified as ACTC for OS X 10.4 Tiger is not an ACTC for 10.6 Snow Leopard. Recertification exams are available to speed the process of moving from one version to the next. OS X 10.6 exams were only available until 31 May 2012, when they were withdrawn.
Apple Certified Technical Coordinator (ACTC)[edit]
This certification is designed for system administrators who provide support to OS X users, as well as maintain the OS X Server platform.
- Required exams
- OS X Support Essentials v10.6 through v10.10
- OS X Server Essentials v10.6 through v10.10
The ACTC certification pathway was withdrawn for new students in 2015.
Apple Certified System Administrator (ACSA)[edit]
This certification is catered for system administrators managing large multiplatform IT networks using Mac OS X Server and other Apple technologies. The ACSA program has been changed to offer individuals more flexibility and is now focused on individual job functions. Each passed exam earns a specialization certificate and a specific number of credits toward ACSA certification, which requires a total of 7 valid (unexpired) credits. OS X 10.6 is the last version to have this certification, there is no equivalent for OS X 10.7 Lion.
- Required exams
- Mac OS X Server Essentials v10.6 (Prometric exam: #9L0-510, withdrawn May 31, 2012)
- Mac OS X Deployment v10.6 (Prometric exam: #9L0-623, withdrawn May 31, 2012)
- Mac OS X Directory Services v10.6 (Prometric exam: #9L0-624, withdrawn May 31, 2012)
- Mac OS X Security & Mobility v10.6 (Prometric exam: #9L0-625, withdrawn May 31, 2012)
Apple Certified Media Administrator (ACMA)[edit]
Examination Mac Os 11
Verifies in-depth knowledge of Xsan architecture, including an ability to install and configure systems, architect and maintain networks, customize and troubleshoot services, and integrate Mac OS X, Final Cut Server, and other Apple technologies within an Xsan installation. ACMA certification is for system administrators and technicians working for resellers, post houses, studios or other large facilities. To earn ACMA status, students must pass three required exams and one elective exam as outlined below.
- Required Exams
- Mac OS X Server Essentials v10.6 (Prometric exam: #9L0-510)
- Xsan 2 Administration (Prometric exam: #9L0-622, withdrawn May 31, 2012)
- Final Cut Server Level One (Prometric exam: #9L0-980)
Plus one of the following:
- Mac OS X Support Essentials v10.6 (Prometric exam: #9L0-403, withdrawn May 31, 2012)
- Mac OS X Directory Services v10.6 (Prometric exam: #9L0-624, withdrawn May 31, 2012)
- Mac OS X Deployment v10.6 (Prometric exam: #9L0-623, withdrawn May 31, 2012)
- Final Cut Pro Level One (Prometric exam: #9L0-827)
- Apple Certificate Support Pro (ACSP 10.11) OS X El Capitan (iLearn: Advance ACSP resource)
Xsan 2 Administrator[edit]
Verifies comprehensive knowledge of Apple's SAN file system for Mac OS X. An Xsan Administrator is responsible for the life cycle of Xsan, including installation, deployment, infrastructure. To earn Xsan Administrator certification, students must pass one exam. Xsan 2 exams are only available until 31 May 2012, when they will be withdrawn following Apple's integration of Xsan into OS X Server 10.7.

- Required Exam
- Xsan 2 Administration (Prometric exam: #9L0-622, withdrawn May 31, 2012)
Associate Certifications[edit]
Certified Associate certifications are designed for professionals, educators and students to validate their skills in Apple's digital lifestyle and authoring applications and iWork.
Apple Certified Associate in iWork[edit]
- Required exam
- iWork Level One (Prometric exam: #9L0-806)
Examination Mac Os X
List of Apple certification programs[edit]
- Apple Authorized Training Centers (AATC)
Hardware[edit]
- Apple Certified Macintosh Technician (ACMT)
- Apple Certified Desktop Technician (ACDT)
- Apple Certified Portable Technician (ACPT)
Trainers and Training Centers[edit]
- Apple Certified Trainer (ACT)
- Apple Authorized Training Centers (AATCs)
- Apple Authorized Training Centers for Education (AATCEs)
Software Certifications[edit]
- Apple Certified Pro
- Xsan for Pro Video
- Apple Certified Master Pro
Mac OS X and IT certifications[edit]
- Apple Certified Support Professional (ACSP)
- Apple Certified Technical Coordinator (ACTC)
- Apple Certified System Administrator (ACSA)
- Apple Certified Specialist (ACS)
- Apple Certified Media Administrator (ACMA)
- Xsan 2 Administrator
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^'Apple - Apple Certified Mac Technician'. Archived from the original on 2010-07-25. Retrieved 2010-09-08.
- ^[1]
- ^https://support.apple.com/en-in/HT204682 Apple - Apple Certified Mac Technician (ACMT) 2015 Frequently Asked Questions
External links[edit]
To use a keyboard shortcut, press and hold one or more modifier keys and then press the last key of the shortcut. For example, to use Command-C (copy), press and hold the Command key, then the C key, then release both keys. Mac menus and keyboards often use symbols for certain keys, including modifier keys:
On keyboards made for Windows PCs, use the Alt key instead of Option, and the Windows logo key instead of Command.
Examination Mac Os Download
Some keys on some Apple keyboards have special symbols and functions, such as for display brightness , keyboard brightness , Mission Control, and more. If these functions aren't available on your keyboard, you might be able to reproduce some of them by creating your own keyboard shortcuts. To use these keys as F1, F2, F3, or other standard function keys, combine them with the Fn key.
Cut, copy, paste, and other common shortcuts
- Command-X: Cut the selected item and copy it to the Clipboard.
- Command-C: Copy the selected item to the Clipboard. This also works for files in the Finder.
- Command-V: Paste the contents of the Clipboard into the current document or app. This also works for files in the Finder.
- Command-Z: Undo the previous command. You can then press Shift-Command-Z to Redo, reversing the undo command. In some apps, you can undo and redo multiple commands.
- Command-A: Select All items.
- Command-F: Find items in a document or open a Find window.
- Command-G: Find Again: Find the next occurrence of the item previously found. To find the previous occurrence, press Shift-Command-G.
- Command-H: Hide the windows of the front app. To view the front app but hide all other apps, press Option-Command-H.
- Command-M: Minimize the front window to the Dock. To minimize all windows of the front app, press Option-Command-M.
- Command-O: Open the selected item, or open a dialog to select a file to open.
- Command-P: Print the current document.
- Command-S: Save the current document.
- Command-T: Open a new tab.
- Command-W: Close the front window. To close all windows of the app, press Option-Command-W.
- Option-Command-Esc: Force quit an app.
- Command–Space bar: Show or hide the Spotlight search field. To perform a Spotlight search from a Finder window, press Command–Option–Space bar. (If you use multiple input sources to type in different languages, these shortcuts change input sources instead of showing Spotlight. Learn how to change a conflicting keyboard shortcut.)
- Control–Command–Space bar: Show the Character Viewer, from which you can choose emoji and other symbols.
- Control-Command-F: Use the app in full screen, if supported by the app.
- Space bar: Use Quick Look to preview the selected item.
- Command-Tab: Switch to the next most recently used app among your open apps.
- Shift-Command-5: In macOS Mojave or later, take a screenshot or make a screen recording. Or use Shift-Command-3 or Shift-Command-4 for screenshots. Learn more about screenshots.
- Shift-Command-N: Create a new folder in the Finder.
- Command-Comma (,): Open preferences for the front app.
Sleep, log out, and shut down shortcuts
You might need to press and hold some of these shortcuts for slightly longer than other shortcuts. This helps you to avoid using them unintentionally.
- Power button: Press to turn on your Mac or wake it from sleep. Press and hold for 1.5 seconds to put your Mac to sleep.* Continue holding to force your Mac to turn off.
- Option–Command–Power button* or Option–Command–Media Eject : Put your Mac to sleep.
- Control–Shift–Power button* or Control–Shift–Media Eject : Put your displays to sleep.
- Control–Power button* or Control–Media Eject : Display a dialog asking whether you want to restart, sleep, or shut down.
- Control–Command–Power button:* Force your Mac to restart, without prompting to save any open and unsaved documents.
- Control–Command–Media Eject : Quit all apps, then restart your Mac. If any open documents have unsaved changes, you will be asked whether you want to save them.
- Control–Option–Command–Power button* or Control–Option–Command–Media Eject : Quit all apps, then shut down your Mac. If any open documents have unsaved changes, you will be asked whether you want to save them.
- Control-Command-Q: Immediately lock your screen.
- Shift-Command-Q: Log out of your macOS user account. You will be asked to confirm. To log out immediately without confirming, press Option-Shift-Command-Q.
Golden dolphin slot. * Does not apply to the Touch ID sensor.
Finder and system shortcuts
- Command-D: Duplicate the selected files.
- Command-E: Eject the selected disk or volume.
- Command-F: Start a Spotlight search in the Finder window.
- Command-I: Show the Get Info window for a selected file.
- Command-R: (1) When an alias is selected in the Finder: show the original file for the selected alias. (2) In some apps, such as Calendar or Safari, refresh or reload the page. (3) In Software Update preferences, check for software updates again.
- Shift-Command-C: Open the Computer window.
- Shift-Command-D: Open the desktop folder.
- Shift-Command-F: Open the Recents window, showing all of the files you viewed or changed recently.
- Shift-Command-G: Open a Go to Folder window.
- Shift-Command-H: Open the Home folder of the current macOS user account.
- Shift-Command-I: Open iCloud Drive.
- Shift-Command-K: Open the Network window.
- Option-Command-L: Open the Downloads folder.
- Shift-Command-N: Create a new folder.
- Shift-Command-O: Open the Documents folder.
- Shift-Command-P: Show or hide the Preview pane in Finder windows.
- Shift-Command-R: Open the AirDrop window.
- Shift-Command-T: Show or hide the tab bar in Finder windows.
- Control-Shift-Command-T: Add selected Finder item to the Dock (OS X Mavericks or later)
- Shift-Command-U: Open the Utilities folder.
- Option-Command-D: Show or hide the Dock.
- Control-Command-T: Add the selected item to the sidebar (OS X Mavericks or later).
- Option-Command-P: Hide or show the path bar in Finder windows.
- Option-Command-S: Hide or show the Sidebar in Finder windows.
- Command–Slash (/): Hide or show the status bar in Finder windows.
- Command-J: Show View Options.
- Command-K: Open the Connect to Server window.
- Control-Command-A: Make an alias of the selected item.
- Command-N: Open a new Finder window.
- Option-Command-N: Create a new Smart Folder.
- Command-T: Show or hide the tab bar when a single tab is open in the current Finder window.
- Option-Command-T: Show or hide the toolbar when a single tab is open in the current Finder window.
- Option-Command-V: Move the files in the Clipboard from their original location to the current location.
- Command-Y: Use Quick Look to preview the selected files.
- Option-Command-Y: View a Quick Look slideshow of the selected files.
- Command-1: View the items in the Finder window as icons.
- Command-2: View the items in a Finder window as a list.
- Command-3: View the items in a Finder window in columns.
- Command-4: View the items in a Finder window in a gallery.
- Command–Left Bracket ([): Go to the previous folder.
- Command–Right Bracket (]): Go to the next folder.
- Command–Up Arrow: Open the folder that contains the current folder.
- Command–Control–Up Arrow: Open the folder that contains the current folder in a new window.
- Command–Down Arrow: Open the selected item.
- Right Arrow: Open the selected folder. This works only when in list view.
- Left Arrow: Close the selected folder. This works only when in list view.
- Command-Delete: Move the selected item to the Trash.
- Shift-Command-Delete: Empty the Trash.
- Option-Shift-Command-Delete: Empty the Trash without confirmation dialog.
- Command–Brightness Down: Turn video mirroring on or off when your Mac is connected to more than one display.
- Option–Brightness Up: Open Displays preferences. This works with either Brightness key.
- Control–Brightness Up or Control–Brightness Down: Change the brightness of your external display, if supported by your display.
- Option–Shift–Brightness Up or Option–Shift–Brightness Down: Adjust the display brightness in smaller steps. Add the Control key to this shortcut to make the adjustment on your external display, if supported by your display.
- Option–Mission Control: Open Mission Control preferences.
- Command–Mission Control: Show the desktop.
- Control–Down Arrow: Show all windows of the front app.
- Option–Volume Up: Open Sound preferences. This works with any of the volume keys.
- Option–Shift–Volume Up or Option–Shift–Volume Down: Adjust the sound volume in smaller steps.
- Option–Keyboard Brightness Up: Open Keyboard preferences. This works with either Keyboard Brightness key.
- Option–Shift–Keyboard Brightness Up or Option–Shift–Keyboard Brightness Down: Adjust the keyboard brightness in smaller steps.
- Option key while double-clicking: Open the item in a separate window, then close the original window.
- Command key while double-clicking: Open a folder in a separate tab or window.
- Command key while dragging to another volume: Move the dragged item to the other volume, instead of copying it.
- Option key while dragging: Copy the dragged item. The pointer changes while you drag the item.
- Option-Command while dragging: Make an alias of the dragged item. The pointer changes while you drag the item.
- Option-click a disclosure triangle: Open all folders within the selected folder. This works only when in list view.
- Command-click a window title: See the folders that contain the current folder.
- Learn how to use Command or Shift to select multiple items in the Finder.
- Click the Go menu in the Finder menu bar to see shortcuts for opening many commonly used folders, such as Applications, Documents, Downloads, Utilities, and iCloud Drive.
Document shortcuts
Examination Cost
The behavior of these shortcuts may vary with the app you're using.
- Command-B: Boldface the selected text, or turn boldfacing on or off.
- Command-I: Italicize the selected text, or turn italics on or off.
- Command-K: Add a web link.
- Command-U: Underline the selected text, or turn underlining on or off.
- Command-T: Show or hide the Fonts window.
- Command-D: Select the Desktop folder from within an Open dialog or Save dialog.
- Control-Command-D: Show or hide the definition of the selected word.
- Shift-Command-Colon (:): Display the Spelling and Grammar window.
- Command-Semicolon (;): Find misspelled words in the document.
- Option-Delete: Delete the word to the left of the insertion point.
- Control-H: Delete the character to the left of the insertion point. Or use Delete.
- Control-D: Delete the character to the right of the insertion point. Or use Fn-Delete.
- Fn-Delete: Forward delete on keyboards that don't have a Forward Delete key. Or use Control-D.
- Control-K: Delete the text between the insertion point and the end of the line or paragraph.
- Fn–Up Arrow: Page Up: Scroll up one page.
- Fn–Down Arrow: Page Down: Scroll down one page.
- Fn–Left Arrow: Home: Scroll to the beginning of a document.
- Fn–Right Arrow: End: Scroll to the end of a document.
- Command–Up Arrow: Move the insertion point to the beginning of the document.
- Command–Down Arrow: Move the insertion point to the end of the document.
- Command–Left Arrow: Move the insertion point to the beginning of the current line.
- Command–Right Arrow: Move the insertion point to the end of the current line.
- Option–Left Arrow: Move the insertion point to the beginning of the previous word.
- Option–Right Arrow: Move the insertion point to the end of the next word.
- Shift–Command–Up Arrow: Select the text between the insertion point and the beginning of the document.
- Shift–Command–Down Arrow: Select the text between the insertion point and the end of the document.
- Shift–Command–Left Arrow: Select the text between the insertion point and the beginning of the current line.
- Shift–Command–Right Arrow: Select the text between the insertion point and the end of the current line.
- Shift–Up Arrow: Extend text selection to the nearest character at the same horizontal location on the line above.
- Shift–Down Arrow: Extend text selection to the nearest character at the same horizontal location on the line below.
- Shift–Left Arrow: Extend text selection one character to the left.
- Shift–Right Arrow: Extend text selection one character to the right.
- Option–Shift–Up Arrow: Extend text selection to the beginning of the current paragraph, then to the beginning of the following paragraph if pressed again.
- Option–Shift–Down Arrow: Extend text selection to the end of the current paragraph, then to the end of the following paragraph if pressed again.
- Option–Shift–Left Arrow: Extend text selection to the beginning of the current word, then to the beginning of the following word if pressed again.
- Option–Shift–Right Arrow: Extend text selection to the end of the current word, then to the end of the following word if pressed again.
- Control-A: Move to the beginning of the line or paragraph.
- Control-E: Move to the end of a line or paragraph.
- Control-F: Move one character forward.
- Control-B: Move one character backward.
- Control-L: Center the cursor or selection in the visible area.
- Control-P: Move up one line.
- Control-N: Move down one line.
- Control-O: Insert a new line after the insertion point.
- Control-T: Swap the character behind the insertion point with the character in front of the insertion point.
- Command–Left Curly Bracket ({): Left align.
- Command–Right Curly Bracket (}): Right align.
- Shift–Command–Vertical bar ( ): Center align.
- Option-Command-F: Go to the search field.
- Option-Command-T: Show or hide a toolbar in the app.
- Option-Command-C: Copy Style: Copy the formatting settings of the selected item to the Clipboard.
- Option-Command-V: Paste Style: Apply the copied style to the selected item.
- Option-Shift-Command-V: Paste and Match Style: Apply the style of the surrounding content to the item pasted within that content.
- Option-Command-I: Show or hide the inspector window.
- Shift-Command-P: Page setup: Display a window for selecting document settings.
- Shift-Command-S: Display the Save As dialog, or duplicate the current document.
- Shift–Command–Minus sign (-): Decrease the size of the selected item.
- Shift–Command–Plus sign (+): Increase the size of the selected item. Command–Equal sign (=) performs the same function.
- Shift–Command–Question mark (?): Open the Help menu.
Other shortcuts
For more shortcuts, check the shortcut abbreviations shown in the menus of your apps. Every app can have its own shortcuts, and shortcuts that work in one app might not work in another.
- Apple Music shortcuts: Choose Help > Keyboard shortcuts from the menu bar in the Music app.
- Other shortcuts: Choose Apple menu > System Preferences, click Keyboard, then click Shortcuts.
Learn more
- Create your own shortcuts and resolve conflicts between shortcuts
- Change the behavior of the function keys or modifier keys